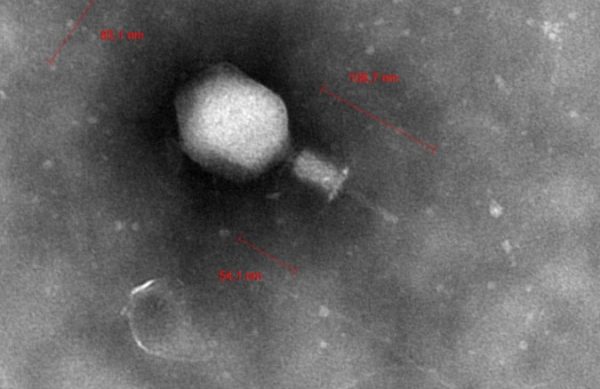
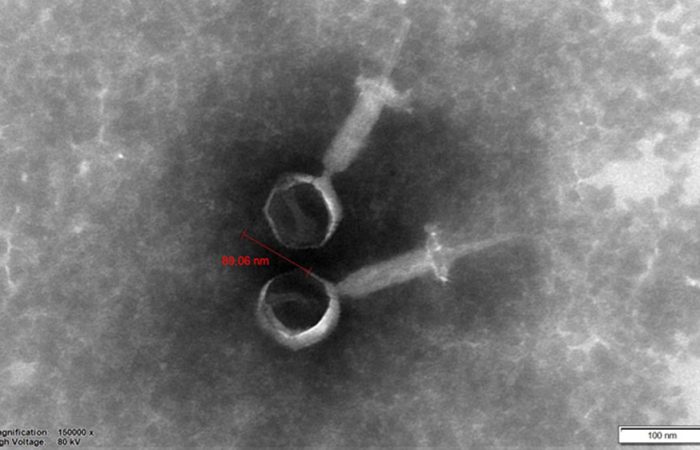
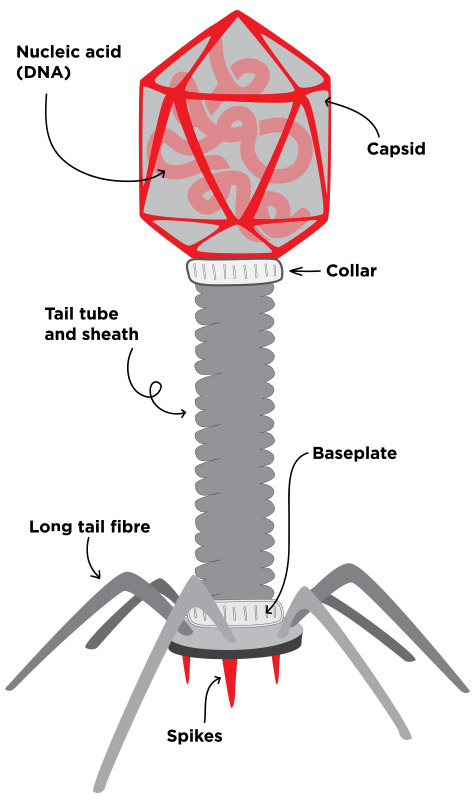
What are bacteriophages?
According to the current knowledge, bacteriophages – known as phages for short – are viruses that exclusively infect bacteria and archaea. Phages are distributed ubiquitously, i.e. everywhere in nature, on plants, animals and humans. The diversity of bacteriophages is infinite, as they can permanently change and adapt to their hosts. The term “bacteriophage” comes from the Greek and literally means “bacteria eater”.
Bacteriophages infect and lyse bacteria very specifically; their binding to the respective bacterium is comparable to the lock-and-key principle.
Many of the bacterial pathogens have zoonotic potential. This means that they can be transmitted between animals and humans in both directions. For some years now, it has been observed worldwide that bacterial infections can only be combated to a limited extent, and in some cases not at all, with antibiotics. Their spread, and thus the spread of antibiotic resistance, usually occurs by the environment. This represents a “One Health Problem”, including a global threat to public health.
Bacteriophages can be an alternative and/or useful additive to antibiotics. They offer many natural advantages in contrast to antibiotics, and at the same time their action is not affected by antibiotic resistance.
 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch